Nipro is dedicated to providing interventional cardiologists with tools to perform delicate lifesaving and life-enhancing procedures to treat patients with heart disease. We use cutting-edge technology as well as the newest techniques, innovative solutions, and complex advancements to reshape intravascular imaging globally. Working hand in hand with physicians, we are focused on providing the best possible care for patients. Nipro is committed to advancing the diagnosis and management of coronary artery disease around the world. This is our contribution to Nipro’s promise to “live longer, live better.”
By offering the only CE Marked and FDA-cleared dual-modality catheter and imaging system indicated for the identification of patients and plaques at increased risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), Nipro provides an invaluable tool for interventional cardiologists to have a concise understanding of the best treatment strategies for the patient.
References
- https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds)
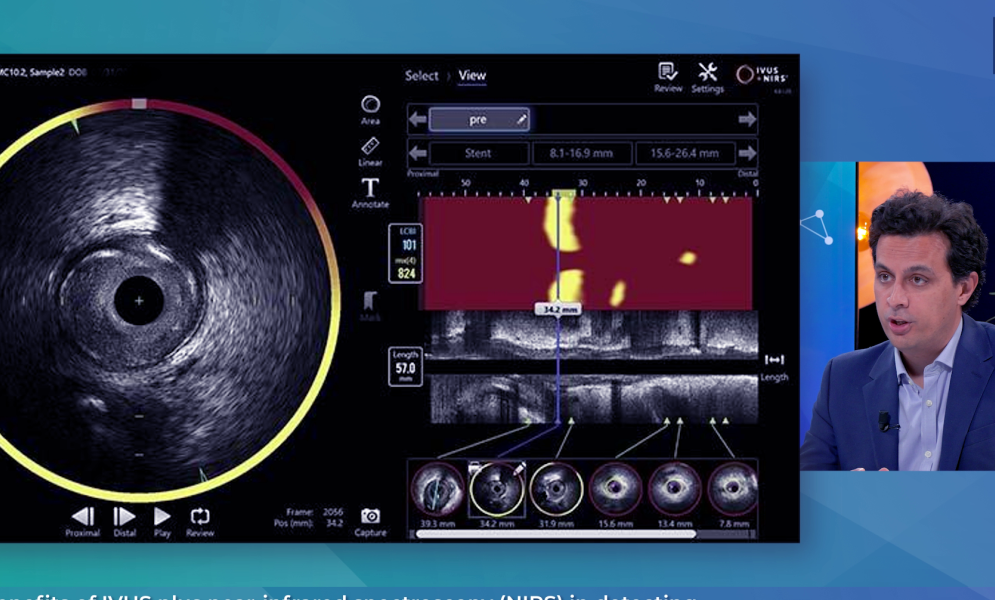
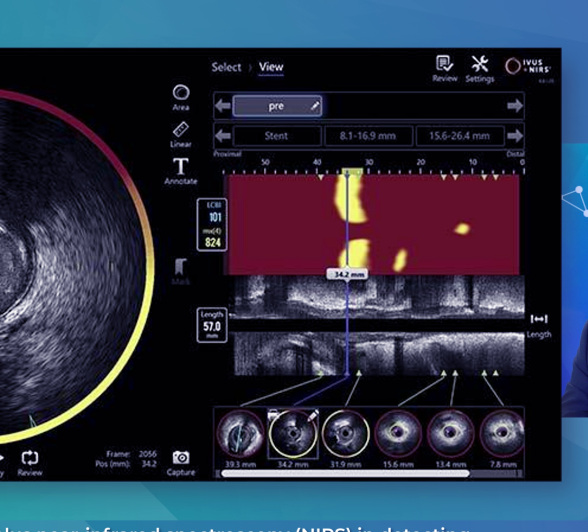
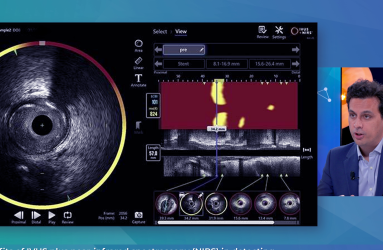
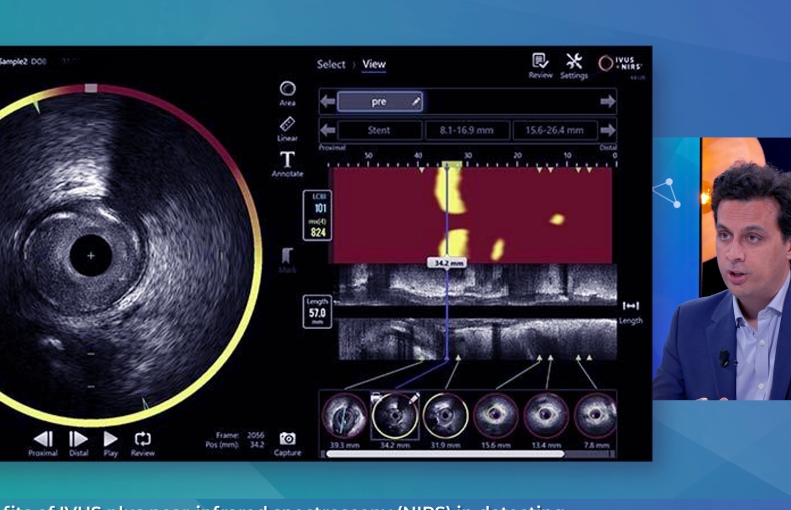
NIRS + IVUS in practice: How dual imaging is shaping precision PCI
A 6-minute clinical conversation recorded at EuroPCR 2025
What if you could see plaque vulnerability, not just vessel structure?
At EuroPCR 2025, Dr. Thomas Keeble (CTC Essex) and Dr. Nilesh Pareek (King’s College London) shared their hands-on experience with a powerful imaging combo: Intravascular Ultrasound (IVUS) + Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS).
Explore our wide selection of Cardiovascular products
From easy-to-use Balloon Catheters to helpful Guide Extensions and revolutionary Intravascular Imaging, we have everything you need to improve your cardiovascular procedures. Explore our innovative solutions now and take your cardiovascular care to the next level.
Diagnostic
Discover our wide range of Diagnostic products
Therapeutic
Discover our wide range of Interventional products
Resources
We are committed to providing comprehensive resources dedicated to supporting medical professionals in utilizing vascular products. Here, you'll find a wealth of valuable information, tools, and materials to enhance your understanding and practice in vascular care.
The Journey of Nipro Cardiovascular
Nipro cardiovascular is dedicated to providing interventional cardiologists with tools to perform delicate lifesaving and life-enhancing procedures to treat patients with heart disease. We use cutting-edge technology as well as the newest techniques, innovative solutions, and complex advancements to reshape intravascular imaging globally, we aim to offer solutions designed to assist doctors in achieving their daily and critical clinical objectives.
Explore Cardiovascular FAQs
Click below to expand and discover commonly asked questions. Explore essential answers about Nipro Cardiovascular. Discover essential answers ranging from easy-to-use Balloon Catheters to helpful Guide Extensions and revolutionary Intravascular Imaging.
Nipro's vascular portfolio offers you unique and advantageous technology to enhance your range of care. From imaging systems and catheters to capture devices, guidewires, balloons, Y-connectors, and inflation devices, Nipro offers solutions designed to help you achieve your daily and critical clinical objectives.
In cardiovascular procedures, a variety of medical device supplies are used to diagnose and treat various conditions. Some common types include:
- Catheters: These are thin, flexible tubes inserted into blood vessels to deliver medications, contrast dye, or devices such as stents or balloons to open blocked arteries.
- Guidewires: Guidewires are thin, flexible wires used to guide catheters and other devices through blood vessels to the target site within the cardiovascular system.
- Balloon Catheters: Balloon catheters have an inflatable balloon at the tip that can be inflated to compress plaque against artery walls during angioplasty procedures, helping to widen the artery and improve blood flow.
- Diagnostic Imaging: Contrast agents, imaging catheters, and imaging systems such as angiography machines and intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) or optical coherence tomography (OCT) are used for visualizing the cardiovascular system during diagnostic and interventional procedures.
- Peripheral Intervention Devices: Devices such as atherectomy devices, thrombectomy devices, and peripheral stents are used to treat blockages or narrowing in arteries outside of the heart, such as those in the legs or arms.
These are just a few examples of the medical device supplies commonly used in cardiovascular procedures. The specific devices and supplies used depend on the nature of the procedure and the patient's condition.
Single- use medical device supplies for cardiovascular care undergo rigorous sterilization processes to ensure patient safety. The sterilization method used depends on the type of device and its materials. Common sterilization methods include:
- Steam Sterilization (Autoclaving): This method uses high-pressure steam to kill microorganisms on medical devices. Devices are placed in a chamber, subjected to steam at high temperature and pressure for a specified time, and then dried. Steam sterilization is suitable for heat-resistant materials like metal instruments.
- Ethylene Oxide (EtO) Sterilization: Ethylene oxide gas is used to sterilize heat-sensitive devices and materials that cannot withstand high temperatures. The devices are placed in a sealed chamber and exposed to EtO gas under controlled conditions for a specified period. After sterilization, the devices undergo aeration to remove residual gas.
- Radiation Sterilization: Gamma radiation or electron beam radiation is used to sterilize disposable medical devices made of plastics, polymers, and other heat-sensitive materials. The devices are exposed to ionizing radiation, which damages the DNA of microorganisms, rendering them non-viable.
- Chemical Sterilization: Chemical agents such as hydrogen peroxide gas plasma or peracetic acid are used to sterilize certain medical devices. These methods are suitable for heat-sensitive devices and involve exposure to sterilizing chemicals in a sealed chamber.
The packaged and sterilized, medical device supplies are stored in a controlled environment to maintain their sterility until use. Key considerations for storage include:
- Clean Environment: Devices should be stored in a clean, dry environment free from dust, moisture, and other contaminants.
- Temperature and Humidity Control: Storage areas should maintain appropriate temperature and humidity levels to prevent degradation of materials and growth of microorganisms.
- Packaging Integrity: Sterile packaging should remain intact to prevent contamination of the devices. Packages should be checked for integrity before use, and damaged or compromised packages should be discarded.
- Monitoring of Expiration Date: Sterile supplies have expiration dates, and healthcare facilities should monitor inventory to ensure that supplies are used before they expire. Expired supplies should be removed from inventory and replaced with fresh stock.
- Organization and Rotation: Supplies should be organized and stored in a way that facilitates easy access and rotation to ensure that older supplies are used first (first-in, first-out principle).
By adhering to proper sterilization and storage procedures, healthcare facilities can ensure the safety of medical device supplies used in cardiovascular care.
Interventional cardiology is a field characterized by ongoing advancements aimed at improving patient outcomes, expanding treatment options, and enhancing procedural safety. Some of the key advancements being made include:
- Innovations in Stent Technology: Advancements in stent design, materials, and drug coatings are improving stent performance and reducing the risk of complications such as restenosis and thrombosis. Bioresorbable stents, which gradually dissolve after implantation, are being developed to address long-term concerns associated with permanent metal stents.
- Image-Guided Interventions: Technologies such as IVUS, OCT, and fractional flow reserve (FFR) measurements provide detailed imaging and functional assessment of coronary arteries during interventions, enabling more precise diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Robotic-Assisted Procedures: Robotic-assisted platforms are being developed to assist interventional cardiologists in performing complex procedures with greater precision and control. These systems offer enhanced maneuverability and dexterity, potentially reducing radiation exposure and improving procedural outcomes.
- Transcatheter Valve Therapies: Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) and transcatheter mitral valve repair/replacement (TMVR) techniques are revolutionizing the treatment of valvular heart disease, offering minimally invasive alternatives to traditional open-heart surgery for high-risk patients.
- Structural Heart Interventions: Advancements in devices and techniques for structural heart interventions, such as closure devices for atrial septal defects (ASDs) and patent foramen ovale (PFO), as well as left atrial appendage (LAA) occlusion devices for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation patients, are expanding treatment options for various cardiac conditions.
- Drug-Coated Balloons: Drug-coated balloons deliver anti-restenotic medications directly to the vessel wall during angioplasty, reducing the risk of restenosis compared to conventional angioplasty balloons. These devices are particularly useful in treating complex lesions and small vessels.
- Next-Generation Imaging Modalities: Emerging imaging technologies, including three-dimensional (3D) rotational angiography, fusion imaging combining angiography with other imaging modalities, and artificial intelligence (AI)-based image analysis, are enhancing visualization and procedural planning in interventional cardiology.
- Remote Monitoring and Telemedicine: Remote monitoring systems and telemedicine platforms enable cardiologists to monitor patients' cardiac health remotely, providing timely interventions and improving post-procedural care, particularly for patients with chronic conditions or those living in remote areas.
These advancements represent just a few examples of the ongoing innovation in interventional cardiology aimed at improving patient care and outcomes. As technology continues to evolve, the field is likely to see further progress in minimally invasive techniques, personalized treatment approaches, and the integration of digital health solutions.
For information regarding Nipro products, services, and resource material:
| E-mail us [email protected] |
|
Submit a detailed inquiry: |
View our manufacturing locations: |